Message Server
The task of the message server is to inform all the servers (instances) belonging to an SAP System of the existence of the other servers. It can also be contacted by other clients (for example, SAPlogon, RFC clients with load balancing) to get information about load balancing.
The SAP Message Server runs as a separate process mostly on the same host as the central instance.
Only one message server can run on each SAP System.
If the messages server stops working, it must be restarted as quickly as possible, to ensure system continues to operate trouble-free.
Monitoring the Message Server in the SAP System
To monitor the message server, you can use the Message Server Monitor (transaction SMMS) in the SAP System. You can check and change all the important settings, create and view traces, read statistics, and so on.
Monitoring the Message Server from the Browser
You can display details of the servers and logon groups from the Web browser too. To do this, in the URL use the host of the message server and the HTTP port of the message server (profile parameterms/server_port_<xx>).
Monitoring and Testing the Message Server at Operating System Level
To monitor the message server at operating system level you need access to the host on which the message server is running. You can log on here with user <sid>adm.
At operating system level there are various programs available, which are delivered with the standard system.
You will usually find the test programs in the executable directory /usr/sap/<SID>/SYS/exe/run.
SAP Web Dispatcher
Purpose
The SAP Web dispatcher lies between the Internet and your SAP System. It is the entry point for HTTP(s) requests into your system, which consists of one or more Web application servers. As a "software web switch", the SAP Web dispatcher can reject or accept connections. When it accepts a connection, it balances the load to ensure an even distribution across the servers.
You can use the SAP Web dispatcher in ABAP/Java systems and in pure Java systems, as well as in pure ABAP systems.
Recommendation
It is also beneficial to use the SAP Web dispatcher, if you do not need security functions (entry point in the DMZ, SSL, URL filtering), but you simply want to balance the load between several SAP Web AS instances.
Introductory Comments
The SAP Web dispatcher is recommended when you use an SAP system with several SAP Web Application Servers for Web applications.
The SAP Web dispatcher is a program that you can run on the machine that is connected directly to the Internet. It requires minimal configuration - you just have to enter the following data in the profile file:
· Port, on which the HTTP(s) requests are to be received (parameter icm/server_port_<xx>)
· Host and HTTP port of the SAP message server (parameter rdisp/mshost and parameter ms/http_port)
Example
If you want to be able to call the Web application externally, for example using the URL www.shop.acme.com, this host name must be mapped internally to the SAP Web dispatcher. This then forwards the HTTP(S) request to a suitable SAP Web AS.
Functions
The SAP Web dispatcher performs the following tasks:
· Selects an appropriate application server (persistence with stateful applications, load balancing, ABAP or Java server), see Server Selection and Load Balancing Using the SAP Web Dispatcher.
· Filters URLs – you can define URLs that are to be rejected, see SAP Web Dispatcher as a URL Filter
· Depending on the SSL configuration, forwards, terminates, and (re)encrypts requests. See SAP Web Dispatcher and SSL
Restrictions
The SAP Web dispatcher is only useful in the Web environment. In the classic SAP system, load is balanced by the message server.
The SAP Web dispatcher forwards only incoming HTTP(S) requests to the Web application server and the response is then returned to the client.
Outgoing requests (such as requests to a different SAP Web Application Server) are not sent via the SAP Web dispatcher. They are sent via the proxy server for the appropriate intranet.
Source: https://help.sap.com/
Why do we do Index rebuild?
Fragmented index results in increased usage of database space and more blocks being read into the buffer. This can be avoided by rebuilding the index.
One can measure index fragmentation using the report RSORATAD or using DB02 --> Detailed Analysis --> Enter Index --> Detailed Analysis --> Analyze Index --> Storage Quality. If storage quality is less than 50% you may need to reorg the index.
If you wish to run an analysis on all the indexes, run the report RSORAISQN. Check SAP note 970538 for more details for more information on the restriction with using this report. Do not run the report without reading the note. You can also get an idea on the amount of fragmentation by comaring the size of the table and the index. If the size of the index is larger than that of the table, the index is fragmented.
Source: sapnwnewbie.blogspot.com
Check status of Business Process Engine (BPE) via SWF_XI_ADM_BPE_DISP
Recently I got an issue that one of our XI production system’s Business Process is not working correctly.
So to check the Business Process status we can use the TCode : SWF_XI_ADM_BPE_DISP or SWF_XI_ADM_BPE
Below is the screenshot of tcode SWF_XI_ADM_BPE_DISP
Here in the below screen, we can see that all the BPE components are running (green status) along with the BPE status.

The status display shows the status of the BPE and its components.
- Green: Component running
- Red: Component stopped
- Amber: Component currently being stopped or started
- Error icon: Error when starting or stopping the component.
We need to have below 2 roles for accessing these tcodes:
- SAP_XI_BPE_MONITOR_ABAP
- SAP_XI_BPE_ADMINISTRATOR_ABAP
http://<host name> <j2ee port>/rwb
Go to Component Monitor in Runtime Workbench. Now select Integration Server > Business Process Engine
Transport Tables form one SAP System to another SAP System
Lets say we have to transport below mentioned systems from one SAP system to another.
/SAPAPO/ATYPES
/SAPAPO/ATUID
/SAPAPO/ATYPEST
Note: Client must be opened for this
Method 1:
Go to TCode: /nsm30
Enter the table name and keep all the settings as it is.

After entering click on display button
Now go to the change mode
Select all

Go to Table View menu and click Transport

Now it will prompt for transport request.
Either select the “Own Request” which is already created by you else create a new transport request right now (depending on the condition)

Click Include in Request
Now we can see a message as shown below.
Then Save
*****************************************************************************************
Method 2
Go to SE10 TCode
Create a new transport
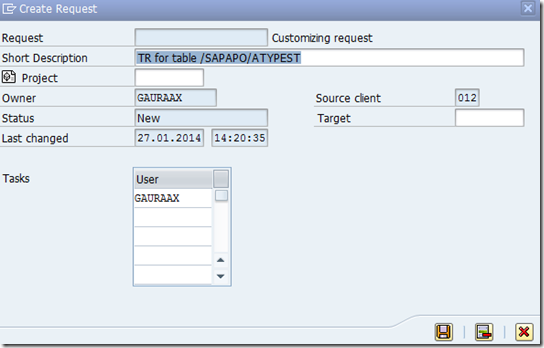
Double click and go inside the TR as shown in below screen.

Add program ID, Object Type and Object Name manually.
We can check table via SE16

Click on execute button present on top.
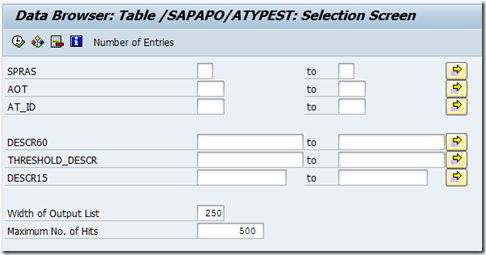
Now we can select all by giving field as *012*

So it means that it will take all those fields who is having mandit as 012.
How to delete released Transport Request from SAP system?
Go to TCode SE16

Enter table name E070
Enter Transport Request number and click execute button

Select the Transport Request and double click and go inside
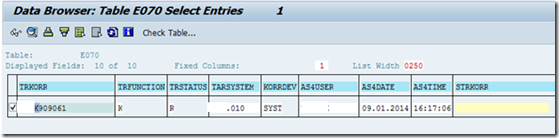
Write /h and hit enter
For going to debugging mode
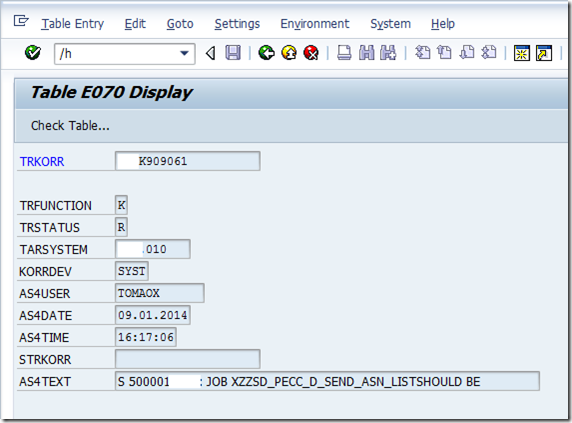
Then we get a notification that ‘Debugging switched On”

Select TRSTATUS and hit enter


Now double click on code

Now it will be shown here

Edit it and change SHOW to DELE (note: it’s not DEL, its DELE)
So now selected transport request got deleted from the system.
Sample SAP BASIS Resume
I have attached one sample resume (only for information purpose)
SAP BASIS Consultants can create their own resume by referring this resume.
- Created users and assigned the roles to the users.
- TMS configuration and Change request management.
- Monitoring Background jobs, re-scheduling, canceling long running jobs
- File system monitoring
- Spool & print management
- Checking Failed update record & system logs
- Short dump analysis, managing lock entries, lock/unlock transaction codes, displaying and monitoring of Database and Application servers, managing user sessions
- Implemented Kernel Upgrade and Applied Support Packs
- Set up Central User Administration (CUA) to manage multiple systems/clients
- Performed Post installation activities for the system landscape.
- Change request transport, Transport management
- Monitoring Background jobs, re-scheduling, canceling long running jobs
- File system monitoring
- Providing Missing Authorizations to the users
- Spool & print management
- Checking Failed update record & system logs
- Short dump analysis, managing lock entries, lock/unlock transaction codes, displaying and monitoring of Database and Application servers, managing user sessions
- Handling Transports from one System to another System. (DEV, QA & PRD)
- Implemented Kernel Upgrade and Applied Support Packs
- Set up Central User Administration (CUA) to manage multiple systems/clients
- CUA for all systems from SOLMAN